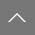Safety / Quality
Process Safety and Disaster Prevention
Targeting Zero Process Accidents
Placing the top priority for management on safety, we have established the Basic Policy on Safety.
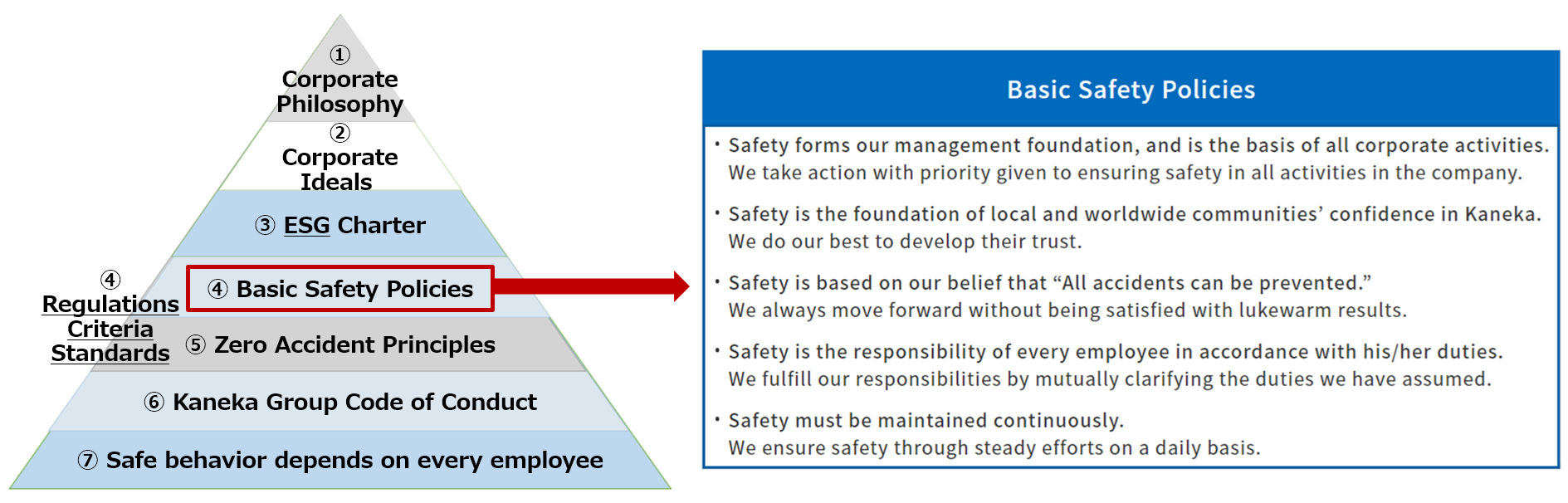
Management and frontline staff are advancing toward our goal of zero occupational accidents, zero process accidents by working to foster a safe culture and ensure the intrinsic safety of equipment, thus inspiring public trust in the safety of our manufacturing sites.
Safe Culture
- Promotion of safety awareness: Communication from management, plant tours by the president, safety management training for plant general managers and production supervisors, review of process disaster risks with guidance from outside experts
- Following the rules: Ensuring adherence to and monitoring basic safety practice (the 3S’s, greetings, handrail holding)
- Development of physical awareness of danger: Hands-on training to heighten sensitivity to danger based on learning through physical experience with virtual reality equipment
Equipment Safety
- Improving equipment safety: We continued equipment improvement (design review) for risks extracted by HAZOP (*1). We revised our plant safety standards to expand target processes and organizations.
- Preventing leaks with multiple layers of protection: To prevent leakage from storage tanks, we revised the KGSS (*2) process safety implementation standards on the storage and handling of chemical substances and initiated risk assessments for all chemical storage facilities.
- Inspection of processing and assembly plants: To strengthen equipment safety measures at processing and assembly-type plants, we conduct inspections to assess the risk of workers getting trapped or caught in equipment. We are promoting further safety measures, including equipment improvements.
*1 HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Studies): A hazard identification technique used for chemical plants.
*2 KGSS (Kaneka Global Safety Standards): A set of standards shared across the Kaneka Group with the aim of ensuring onsite safety and security. We have put in place implementation standards (17 for occupational safety, 7 for process safety, and 1 for emergency response) under the respective management standards for occupational safety, process safety, and emergency response. A major feature of our approach is that each year we carry out gap assessments (of gaps between standards and actual conditions), and fill any gaps with the standards.
Emergency Response Training
We annually conduct comprehensive disaster drills, based on scenarios such as a large-scale earthquake or a fire caused by hazardous material leakage, at all parent manufacturing sites jointly with local governments and local industrial facilities so that we can promptly and effectively respond to emergency situations.
Emergency Response and Evacuation Drills (Examples in fiscal 2022)
| № | Training | Content (Purpose) |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | Undisclosed scenario training | Abnormal events and scenarios are not disclosed in advance. A third party introduces ad-lib elements to train training participants in making on-the-spot judgments and communication methods. |
| (2) | Comprehensive disaster drills | Assuming plant damage, the entire plant participates in these drills, with participation by government representatives. Training often uses undisclosed scenarios from (1). Serves also to convey safety and security to the government. |
| (3) | Drills for nighttime power outages | Training to carry out bare minimum activities in complete darkness (while wearing a headlamp, etc.). |
| (4) | Toxic gas leakage evacuation drills | Evacuation drills positing a chlorine gas leak, including at adjacent plants. Includes evacuating buildings, wearing a gas mask, and practicing gas concentration measurement. |
Comprehensive Disaster Drills
| Manufacturing Site | Date | Participants | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takasago Manufacturing Site | December 19, 2022 | 2,112 | An earthquake resulting in a fire caused by hazardous material leakage |
| Osaka Manufacturing Site | November 17, 2022 | 1,044 | An earthquake resulting in a fire |
| Shiga Manufacturing Site | November 22, 2022 | 363 | An earthquake resulting in a fire |
| Kashima Manufacturing Site | December 14, 2022 | 59 | An earthquake resulting in a fire caused by hazardous material leakage |
We advance countermeasures against natural disasters in order of priority, including promoting the earthquake-proofing of equipment in preparation for large-scale earthquakes, and implementing risk assessment for typhoons, heavy rains and floods, which have frequently occurred in recent years, based on hazard maps for all parent manufacturing sites and Group companies in Japan.
We also learn how to initially respond to a fire and how to use a hydrant to prevent the spread of a fire through daily training to ensure that we can immediately perform self-defense fire-fighting operations.
To constantly improve our disaster coping skills and strengthen anti-disaster activities, we join a hydrant operation competition held locally, ranking higher every year.

Plant Safety Initiatives
We previously conducted a variety of safety management and safety technology training in a group format, targeting newly appointed manufacturing department general managers, section managers, and safety & technology promoting expert. By switching to online venues and distributing audio materials, we have continued to carry out training seamlessly even during the COVID-19 pandemic.
We assess the safety of equipment using HAZOP. We make it compulsory that employees registered as evaluators through the in-house certification program should assess the safety of equipment. To foster safety evaluators, we annually hold a HAZOP workshop, inviting external experts as lecturers.
We have established a technique for assessing the risk of accidental chemical mixing and a method for evaluating thermal runaway in chemical reactions. We will continue to improve these safety techniques to ensure plant safety.
CHECK & ACT
To reduce the number of process accidents, we will work to ensure risk assessment and intrinsic safety by setting risk assessment standards and fostering safety evaluators. We will continue to make company-wide efforts to thoroughly prevent recurrence and similar accidents.